The Sims screenshot
The Sims is released
While most games see a player working towards an end-game scenario, The Sims allows players to create a home, get a job, and form relationships in a free-form world. Designed by a team at Maxis led by Wil Wright, The Sims took concepts from Wright’s previous game Sim City. Characters controlled by the player were customizable, and spoke an artificial language called Simlish. The Sims became exceptionally popular with women, who accounted for more than sixty percent of players.
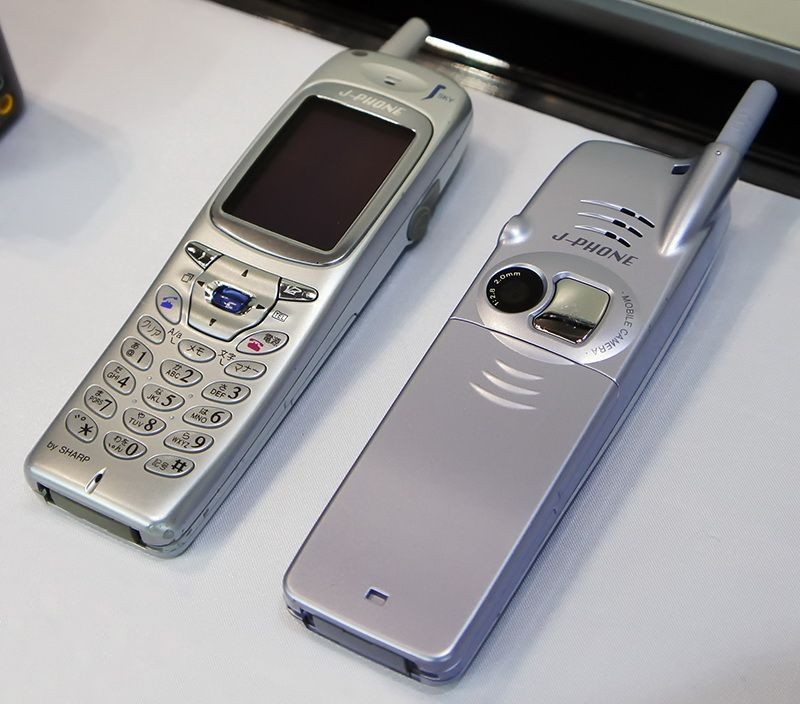

Sony-built J-Phone J-SH04
First camera phone introduced
Japan’s SoftBank introduces the first camera phone, the J-Phone J-SH04; a Sharp-manufactured digital phone with integrated camera. The camera had a maximum resolution of 0.11 megapixels a 256-color display, and photos could be shared wirelessly. The J-Phone line would quickly expand, releasing a flip-phone version just a month later. Cameras would become a significant part of most phones within a year, and several countries have even passed laws regulating their use.
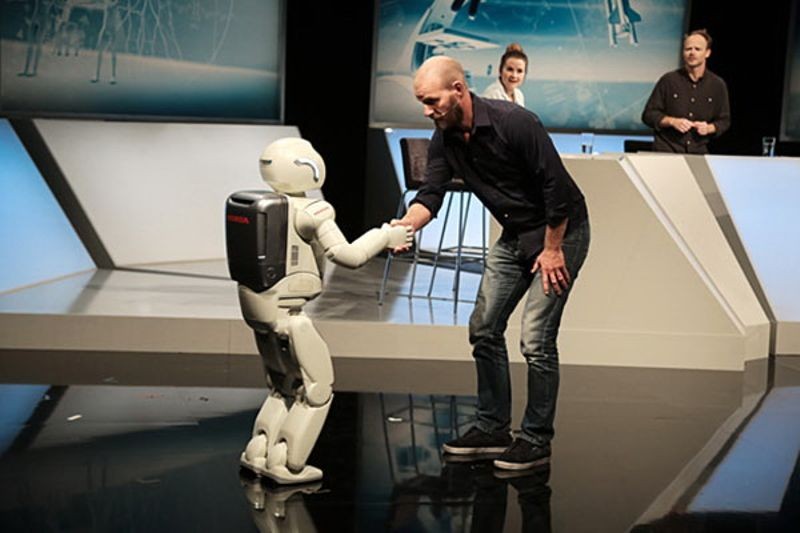

Honda’s Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility (ASIMO) humanoid robot
Honda’s Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility (ASIMO) humanoid robot
Honda’s Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility (ASIMO) humanoid robot is introduced. It could walk 1 mph, climb stairs and change its direction after detecting hazards. Using the camera mounted in its head, ASIMO could also recognize faces, gestures and the movements of multiple objects. Additionally, ASIMO had microphones that allowed it to react to voice commands. About 100 were built.
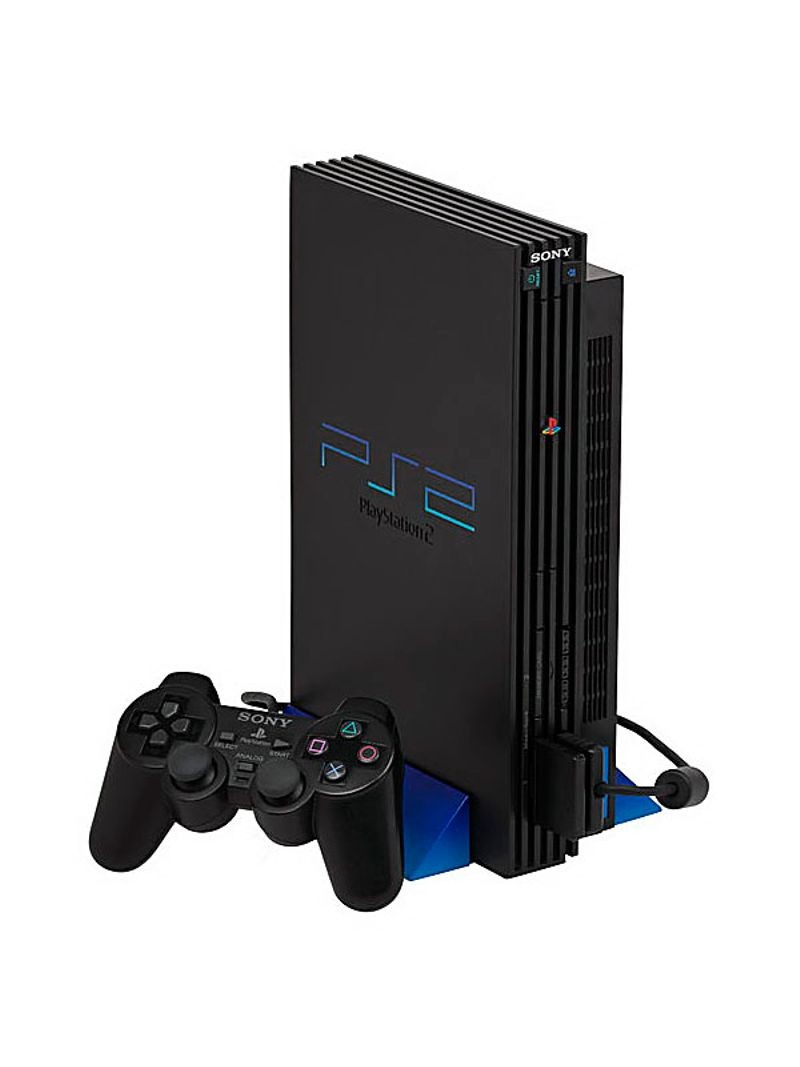

PlayStation 2 game console
Sony releases the PlayStation 2
The PlayStation 2 (PS2) represents a significant change in the concept of game consoles. The PS2 allowed for DVDs to be played as well as game disks, making it more of an entertainment console than a game console. Many consumers bought the PS2 for its DVD player alone, since the PS2 was cheaper than stand-alone DVD players. In turn, this greatly increased consumer adoption of the DVD format. Over more than ten years in active production, the PlayStation 2 has sold more than a hundred and fifty million units, making it one of the most successful game systems ever released.
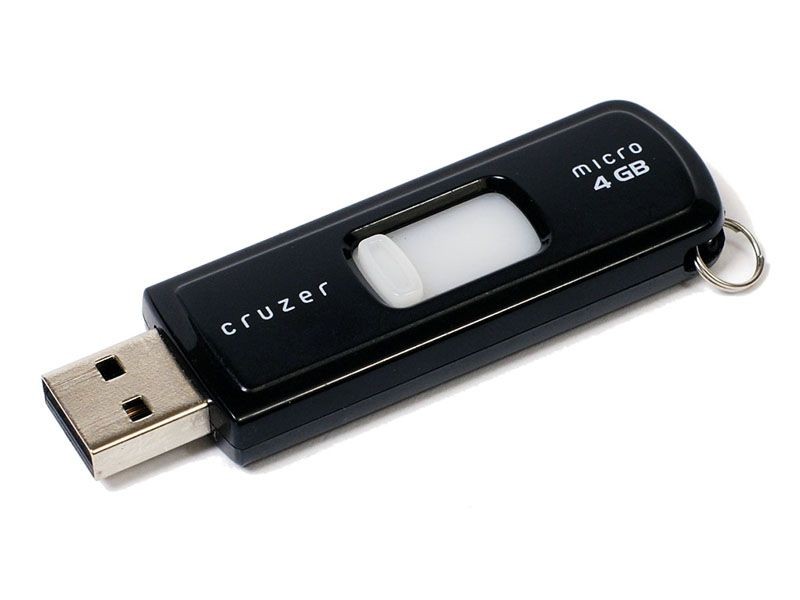

SanDisk 4GB Cruzer flash drive
USB Flash drive
USB Flash drives are introduced. Sometimes referred to as jump drives or memory sticks, these drives consisted of flash memory encased in a small form factor container with a USB interface. They could be used for data storage and in the backing up and transferring of files between various devices. They were faster and had greater data capacity than earlier storage media. Also, they could not be scratched like optical discs and were resilient to magnetic erasure, unlike floppy disks. Drives for floppy disks and optical discs faded in popularity for desktop PCs and laptops in favor of USB ports after flash drives were introduced.

Electronic sign incorrectly displaying the year 1900 on January 3, 2000
Y2K bug
During the late 1990s, the impending Year 2000 (Y2K) bug fuels news reports that the onset of the year 2000 will cripple telecommunications, the financial sector and other vital infrastructure. The issue was rooted in the fact that date stamps in most previously written software used only two digits to represent year information. This meant that some computers might not be able to distinguish the year 1900 from the year 2000. Although there were some minor glitches on New Year’s Day in 2000, no major problems occurred, in part due to a massive effort by business, government and industry to repair their code beforehand.

Bram Cohen
BitTorrent is launched
BitTorrent, a peer-to-peer file sharing service, is launched by BitTorrent, Inc. It was developed by Bram Cohen and was initially an open source program, but became closed source in 2005. BitTorrent enabled users to upload and download files, typically music and movies. It came under scrutiny of copyright holders – such as the music and motion picture industries — which claimed BitTorrent facilitated theft of their intellectual property.

Opening of first Apple Store in Tysons Corner Center
First Apple stores open
Apple’s first retail outlets, one in Tysons Corner, Virginia, and the same day in Glendale, California, open for business. The Apple Store was an innovative shopping experience, with each store built around a common design philosophy, and eventually doing away with the traditional cash register. The Apple Store not only offered Apple’s products, but also software, accessories, and classes on how to use Apple software. The Genius Bar, where customers can obtain support for their Apple products, has also become a major part of each store.

Mac OS X screenshot
Mac OS X is released
Mac OS X is released. It was a significant departure from the classic Mac OS as it was based on the Unix-like operating systems FreeBSD, NetBSD and NeXTSTEP/OpenStep. OS X introduced a more stable and reliable platform and multiple applications could more efficiently be run at the same time. The Mac OS X 10.6 (“Snow Leopard”) update, released in 2009, completed the Mac’s transition from a 32-bit to a 64-bit operating system.
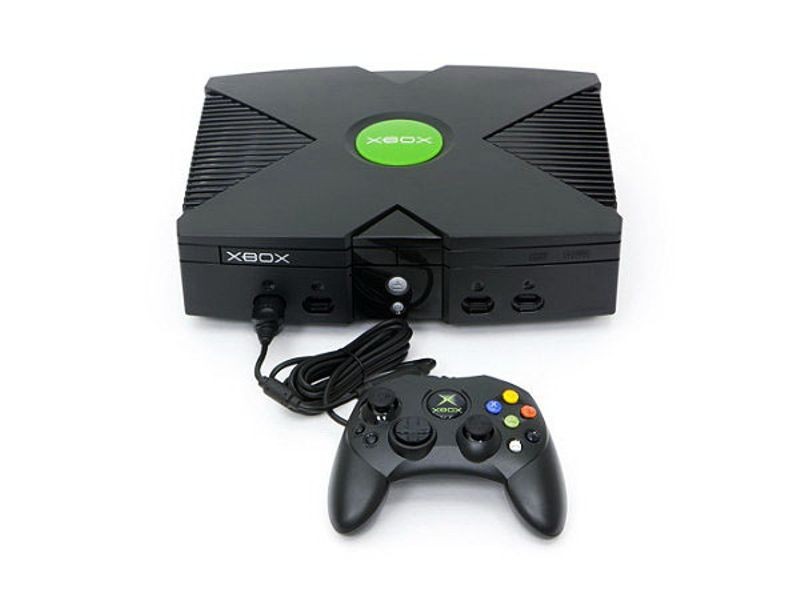

Xbox game console
Microsoft enters gaming arena with Xbox
In 1998, members of Microsoft’s multi-media DirectX team reconfigured old Dell laptops to create a Window-based video game console. They brought the idea to Microsoft management, which approved the idea of a home game console based on Microsoft’s Direct X graphics technology. The Xbox (originally DirectX Box) used standard PC parts, including a built-in hard drive. Seen as a major risk for a software company, the Xbox console surprisingly sold out its initial North American production run. In 2002, Microsoft launched Xbox Live, an online service that allowed competitive gameplay and chat.
The Xbox was hailed for its high-quality graphics. Graphics acceleration was provided by an nVidia-Microsoft co-designed Graphical Processing Unit (GPU) which gave the Xbox the high-performance graphics usually associated with much more powerful processors.

A.I. Artificial Intelligence movie poster
Steven Spielberg’s A.I. Artificial Intelligence released worldwide
Conceived of by legendary director Stanley Kubrick, but directed by Steven Spielberg after Kubrick’s death, A.I. tells the story of David, a humanoid robot that can feel and express emotion. David is purchased by a family whose son Martin is in cryo-stasis until a cure is found for the disease he is afflicted with. David’s “mother,” Monica, reluctantly imprints herself upon him, and he starts to act like a genuine child. When Martin is revived, a series of events leads to David’s abandonment by his family. On his own in a new world, David searches for happiness in a quest to be a real boy.

Greed issue, San Francisco magazine
The Dot Com Boom…and Bust
As users flock to the Web, the opportunities seem boundless. Nearly everything you could do with previous networks is ported to the Web, and every business sector, community, religion, and subculture stakes out a place online. Initial skepticism gives way to experimentation, and then mounting excitement as people begin to believe that the old laws of business don’t apply to this new medium. Nobody wants to be left behind, fueling a frenzy of business ventures—many built on shaky foundations.
In early 2000, business fundamentals reassert themselves. In one year, technology stocks lose about 60% of their value. The boom and bust have their greatest effect in the San Francisco Bay Area, home of Silicon Valley as well as many previous booms from the Gold Rush on.
Windows XP screenshot
Windows XP is released
The Windows XP operating system is released. Based on the Windows NT kernel, XP was considered more stable than previous versions of the operating system. XP was widely adopted by industry and persisted much longer than Microsoft planned. For example, in 2014, 95% of the world’s automated teller machines ran XP. Microsoft support for XP ended on April 8, 2014.
Original iTunes interface
iTunes is released
Apple’s iTunes is released. It was based on Bill Kincaid’s SoundJam MP software, the rights to which Apple purchased. Initially, iTunes was only supported on the Mac operating system and functioned as a media player and media management tool. iTunes allowed users to record music from CDs, bring it into iTunes, mix it with other songs and then burn a custom CD. When the Apple iTunes music store was launched in 2003, it transformed music distribution and the entire music industry. Less than a week after its launch, over one million songs were downloaded. By 2013, over 25 billion songs had been downloaded from the iTunes store.
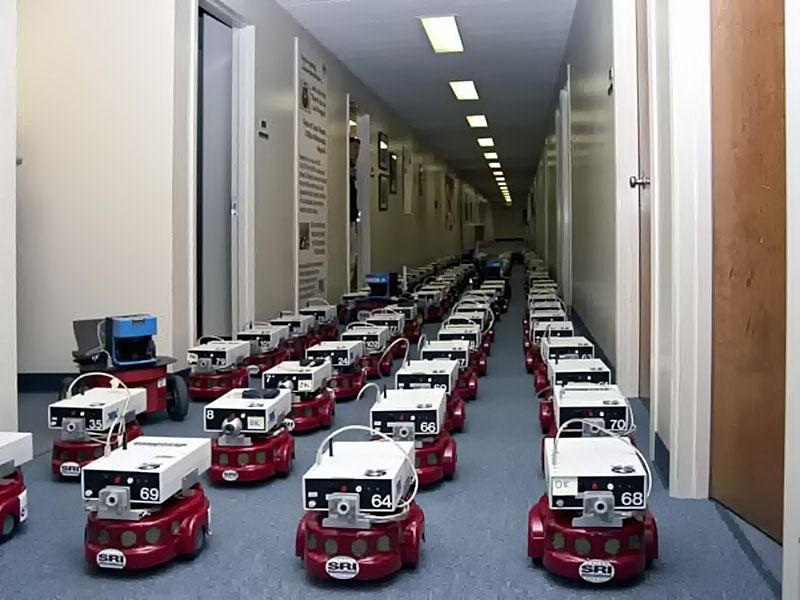

Army of Centibots
DARPA’s Centibots project
The Centibots project, funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), sought to prove that up to 100 robots could survey a potentially dangerous area, build a map in real time, and seek items of interest. Centibots communicated with each other to coordinate their effort. If one robot failed, another took over its task. The robots were completely autonomous, requiring no human supervision.
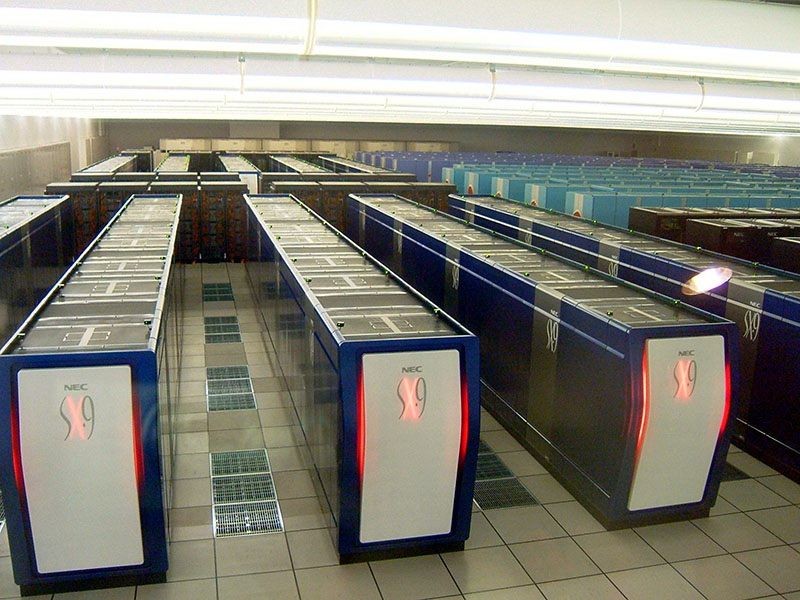

Earth Simulator Supercomputer
Earth Simulator is world’s fastest supercomputer
Developed by the Japanese government to create global climate models, the Earth Simulator is a massively parallel, vector-based system that costs nearly 60 billion yen (roughly $600 million at the time). A consortium of aerospace, energy, and marine science agencies undertook the project, and the system was built by NEC around their SX-6 architecture. To protect it from earthquakes, the building housing it was built using a seismic isolation system that used rubber supports. The Earth Simulator was listed as the fastest supercomputer in the world from 2002 to 2004.
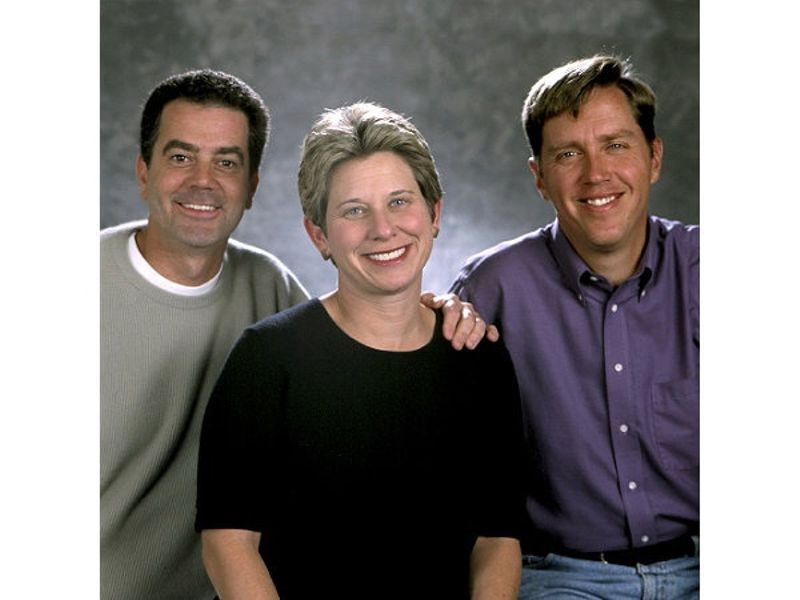

Colligan, Dubinsky, Hawkins (left to right)
Handspring Treo is released
Leaving Palm Inc., Ed Colligan, Donna Dubinsky, and Jeff Hawkins found Handspring. After retiring their initial Visor series of PDAs, Handspring introduced the Treo line of smartphones, designed with built-in keyboards, cameras, and the Palm operating system. The Treo sold well, and the line continued until Handspring was purchased by Palm in 2003.
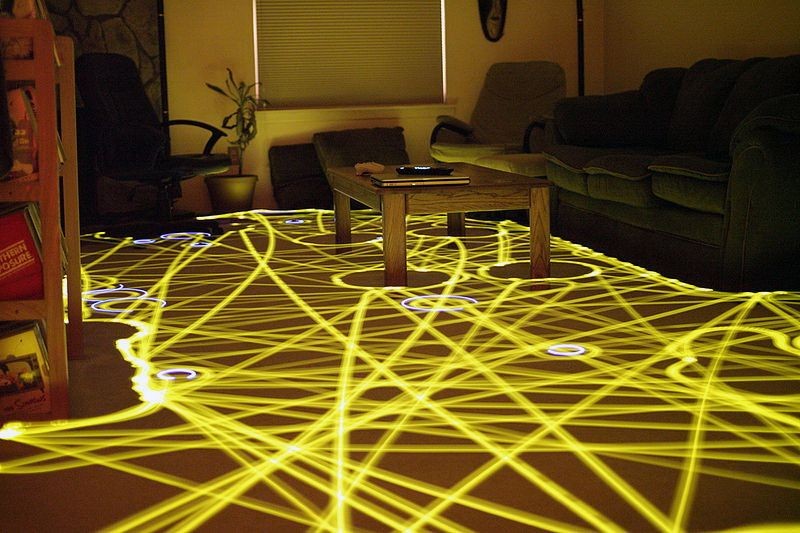

Cleaning path of an iRobot Roomba autonomous vacuum cleaner
The Roomba is introduced
iRobot’s Roomba is introduced. Using a cleaning algorithm, the autonomous robotic vacuum cleaner could clean a room while detecting and avoiding obstacles. Rodney Brooks, co-founder of iRobot, previously performed research at MIT’s Mobile Robotics Lab. The research focused on using insect-like reflex behavior instead of a central “brain” to create purposeful behavior.

Eve OnLine
Eve OnLine is released
Massive Multi-player Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPG) begins to blossom with the advent of faster computers with ever-better graphics. Eve Online allows players to assume command of a spaceship, form alliances, and combat against other players, or the environment. It represented a new concept where skills were gained in real-time, even when a player was not logged into the game. By 2013, more than half-a-million users were regularly playing.

One of the initial Blu-ray releases, The Terminator
Blu-ray optical disc
Developed by a technology industry consortium, the Blu-ray optical disc is released. It was intended to be the successor to the DVD, and was designed to store high definition video at 1080p, while older DVDs were only capable of 480p resolution. The disc was named for the relatively short wavelength blue laser that reads the data on the disc, which was capable of reading data stored at a higher density compared to the red laser used for reading DVDs. A brief storage format battle ensued between Blu-ray and HD DVD, a format that was being supported in an effort spearheaded by Toshiba. Blu-ray ultimately prevailed.

CSAIL logo
CSAIL at MIT is formed
The Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT is formed with the merger of the Laboratory for Computer Science and the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. The AI lab was founded in 1959 by John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky and the Laboratory for Computer Science was opened in 1963 as Project MAC.

MySpace.com original logo
MySpace founded
While neither the first, nor the largest, social network, MySpace is one of the most important and helped define the second wave of social networking. Two eUniverse employees, Chris DeWolfe and Tom Anderson, developed MySpace based around the features of the earlier social networking site, Friendster, and adding features such as file storage and games. By 2005, MySpace had become a major social networking site, eventually acquiring more than 100 million users. Increased competition, and the near-meteoric rise of Facebook, led to MySpace losing market share and value, though many entertainment personalities, and especially musicians, continue to use the platform as their primary web presence.
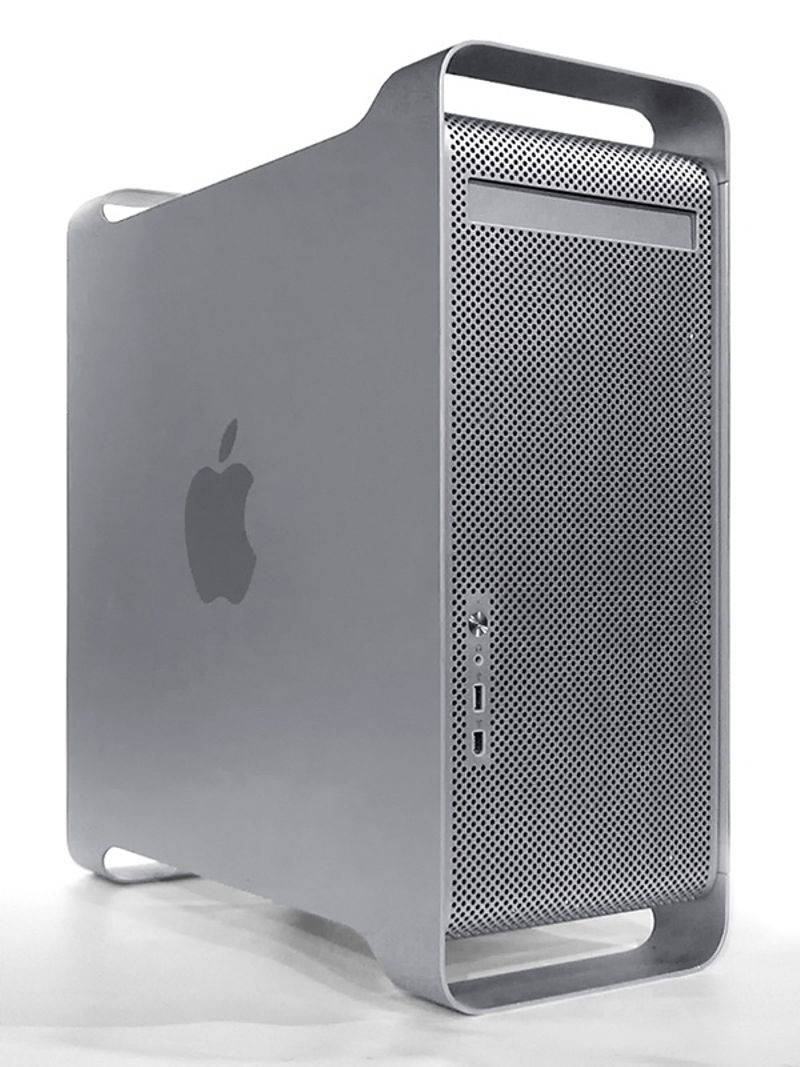

PowerMac G5 tower computer
PowerMac G5 is released
With a distinctive anodized aluminum case, and hailed as the first true 64-bit personal computer, the Apple G5 is the most powerful Macintosh ever released to that point. While larger than the previous G4 towers, the G5 had comparatively limited space for expansion. Virginia Tech used more than a thousand PowerMac G5s to create the System X cluster supercomputer, rated #3 in November of that year on the world’s TOP500 fastest computers.
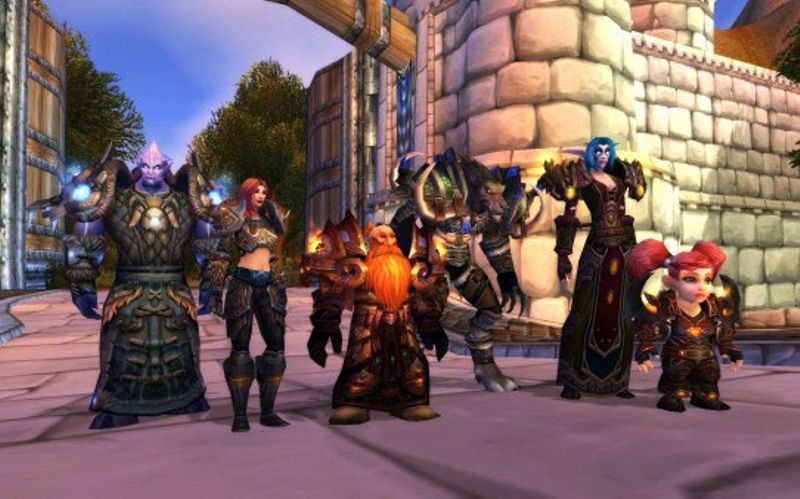
World of Warcraft comes on-line
After ten years as a series of strategy games, Blizzard Entertainment launches World of Warcraft, a Massive Multiplayer Online Role Playing Game (MMORPG) version of their popular Warcraft franchise. Centered on the fantasy world of Azeroth, Warcraft allows players to choose an avatar to go “questing.” Players form guilds and raiding parties, as well as form strong social, and even romantic, connections through the game’s built-in chat function. World of Warcraft has been dominant in the MMORPG market since its release.

Noogler (new Googler) hat worn by fresh recruits
Google’s IPO and the New, Slow Boom
In 2004, Google is the first major Web company to float a publicly traded stock since the go-go days of the dot-com boom. This is a direct result of Google solving the eternal problem plaguing all previous search engines – how to profit from search. The secret turns out to be a discreet form of advertising, based on auctioning off keywords to appear as “sponsored results” within a search results page. Many people take Google’s Initial Public Offering (IPO) as a sign that the Web is not only back from its deep trough after the crash but entering a new period of expansion, and many other IPOs follow Beneath it all, of course, the Web continues to steadily grow as it has since the early 1990s.
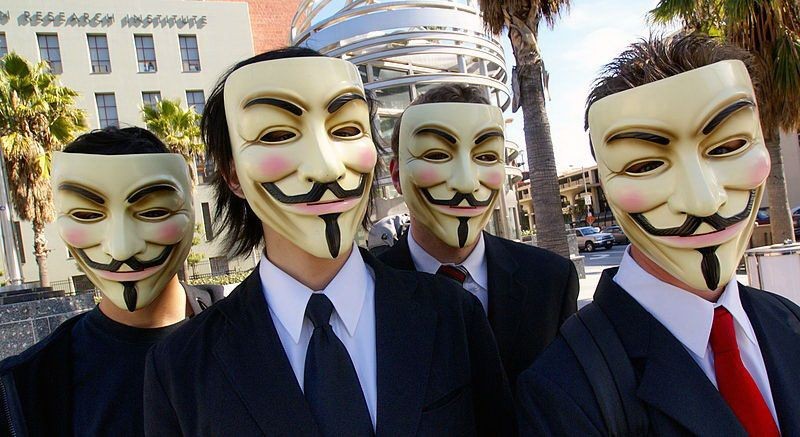
Hacker group Anonymous forms
Forming out of interactions on the image-sharing website 4chan, Anonymous is a loose association of users, many of whom consider themselves ‘hacktivists’. Their activities started as purely digital publicity stunts and protests that included the hacking of websites for groups like the Church of Scientology and the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA). Later targets included many government agencies around the world. In public, many Anonymous affiliates (referred to as Anons) can be identified by their wearing of Guy Fawkes masks.
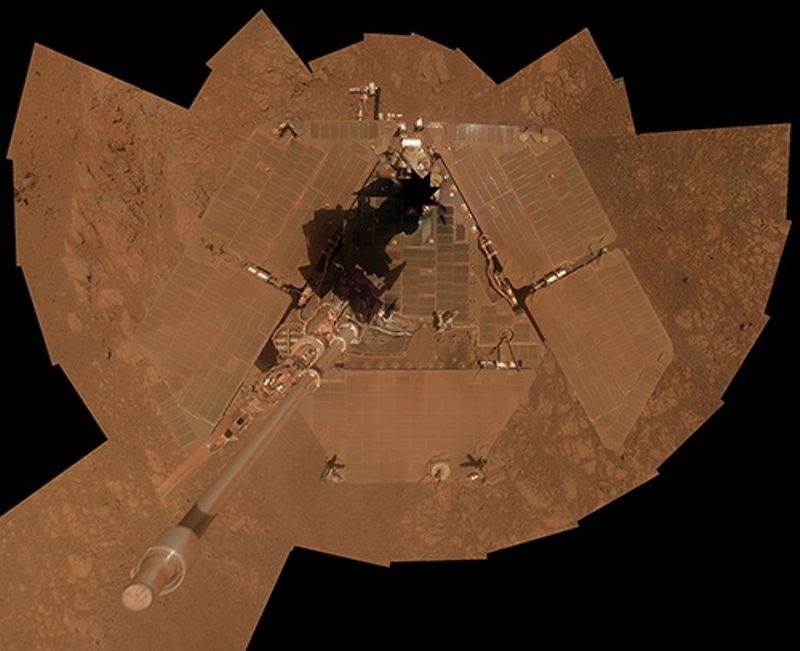

Opportunity self-portrait on Mars
Opportunity and Spirit Mars Rovers land on Mars
Caltech designs both the Opportunity and Spirit Mars Rovers. Both landed in 2004 and ran 20 times longer than their planned lifetime of 90 days. While Spirit ceased to move in 2009 and communications from the rover stopped in 2010, Opportunity far exceeded its expected lifetime.
“Web 2.0” brings back Interactivity
The original Web concept, and many pre-Web systems, had depended heavily on user contributions. Yet many 1990s Web sites had been more like traditional TV or radio broadcasting, with providers feeding content to passive surfers. Partly this had been because dominant Web browsers lacked editing capability. From the early 2000s a number of sites begin helping users generate and shape content: wikis, blogs, social networking sites, and more. Photo and video sharing sites take advantage of the spread of faster Internet connections to let users both upload and browse those media.
O’Reilly and Associates popularizes the name “Web 2.0” with their 2004 conference of that name. Most browsers still don’t support Web page editing, but Web 2.0 sites find various workarounds – from wiki and blogging software to commenting features – to give users a voice.

Arduino starter kit
Arduino
Harkening back to the hobbyist era of personal computing in the 1970s, Arduino begins as a project of the Interaction Design Institute, Ivrea, Italy. Each credit card-sized Arduino board consisted of an inexpensive microcontroller and signal connectors which made Arduinos ideal for use in any application connecting to or monitoring the outside world. The Arduino used a Java-based integrated development environment and users could access a library of programs, called “Wiring,” that allowed for simplified programming. Arduino soon became the main computer platform of the worldwide “Maker” movement.

Hadoop logo
Hadoop is developed
Hadoop is an open source software project initially developed by Google as a means of extracting search results from large amounts of unstructured data, such as data found on the web. It was used by many large corporations where networked scalability, cost effectiveness and fault tolerance were critical to their business models. Companies such as Google, Yahoo, American Airlines, IBM and Twitter all used Hadoop, and it could be scaled from a single server to thousands. With Hadoop different types of data could be seamlessly integrated and Hadoop could redirect work to another system if a node failed in the cluster.

IBM and Lenovo logos
Lenovo acquires IBM’s PC business
Nearly a quarter century after IBM launched their PC in 1981, they had become merely another player in a crowded marketplace. Lenovo, China’s largest manufacturer of PCs, purchased IBM’s personal computer business in 2005, largely to gain access to IBM’s ThinkPad line of computers and sales force. Lenovo became the largest manufacturer of PCs in the world with the acquisition, later also acquiring IBM’s server line of computers.
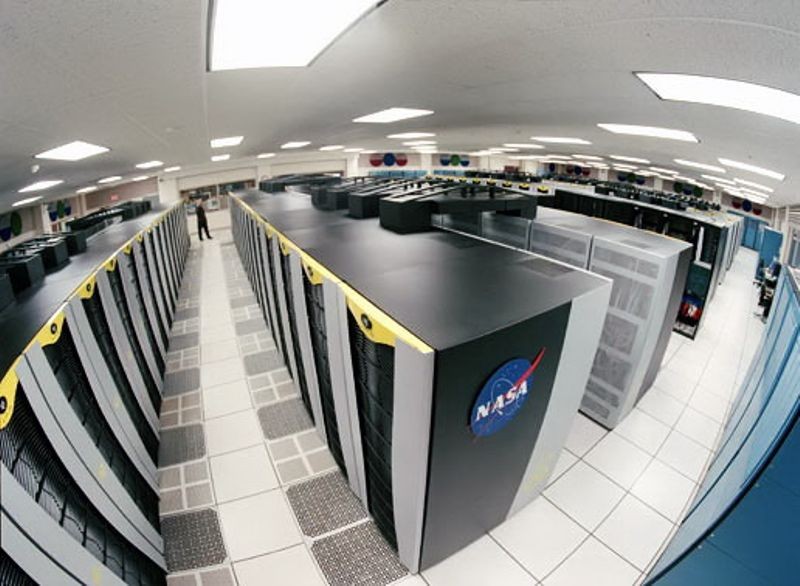

Columbia Supercomputer system made up of SGI Altix
NASA Ames Research Center supercomputer Columbia
Named in honor of the space shuttle which broke-up on re-entry, the Columbia supercomputer is an important part of NASA’s return to manned spaceflight after the 2003 disaster. Columbia was used in space vehicle analysis, including studying the Columbia disaster, but also in astrophysics, weather and ocean modeling. At its introduction, it was listed as the second fastest supercomputer in the world and this single system increased NASA’s supercomputing capacity 10-fold. The system was kept at NASA Ames Research Center until 2013, when it was removed to make way for two new supercomputers.
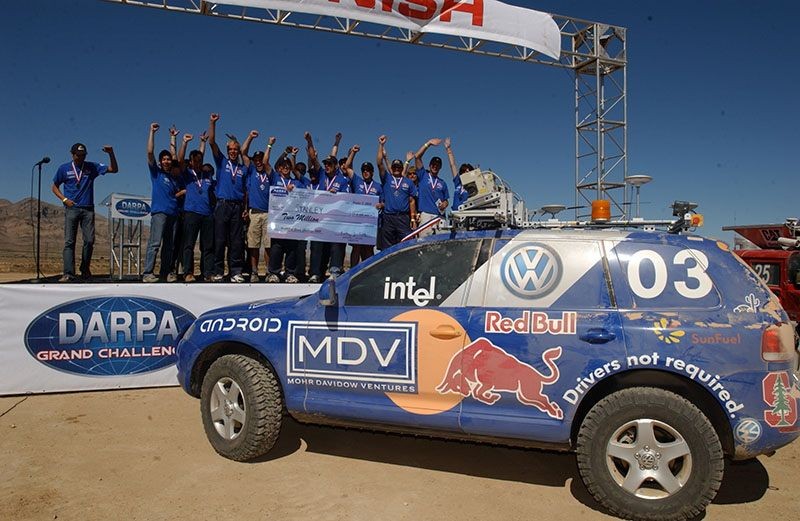

Stanford’s Stanley self-driving vehicle
Stanford’s autonomous vehicle wins 2005 DARPA “Grand Challenge”
Stanford Racing Team’s autonomous vehicle “Stanley” wins the 2005 DARPA “Grand Challenge” held near Las Vegas. Driving autonomously on an off-road, 175-mile long desert course, the Volkswagen Touareg R5 finished the challenge in less than 7 hours with no human intervention–well before the 10 hour time limit. For winning the challenge, the Stanford Racing Team took home $2 million. The DARPA challenges, first introduced in 2004, are intended to spur interest and generate innovation in the area of self-driving cars.

Amazon Web Services Launches Cloud-Based Services
Amazon Web Services is launched. It introduced a number of web services, including Amazon Elastic Cloud 2 (EC2) and Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3). EC2 allowed users to rent virtual time on the cloud to scale server capacity quickly and efficiently while only paying for what was used. Use of the cloud eliminates the need for a company to maintain a complex computing infrastructure on their own. Additionally, it saved space and hassle in the form of less onsite server room square footage. S3 was a cloud-based file hosting service that charged users monthly for the amount of data stored and for the bandwidth of transferring data. Similar services, like Google Drive, followed suit and created their own proprietary services.
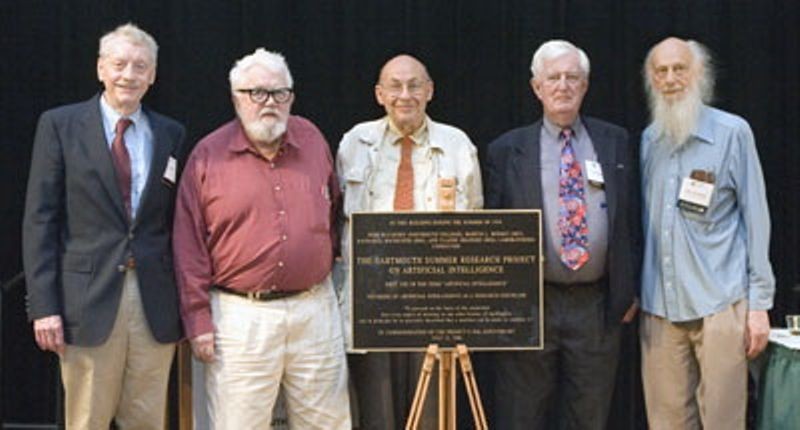

(L to R) Trenchard More, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Oliver Selfridge, and Ray Solomonoff at AI@50
Fiftieth anniversary of seminal artificial intelligence conference
AI@50, the fiftieth anniversary celebration of Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, is held on the Dartmouth College campus. Five attendees of the original conference in 1956 were present at the anniversary–John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Trenchard More, Oliver Selfridge and Ray Solomonoff. The coining of the term “Artificial Intelligence” was credited to the proposal for the original conference, which is viewed as the founding event of AI.
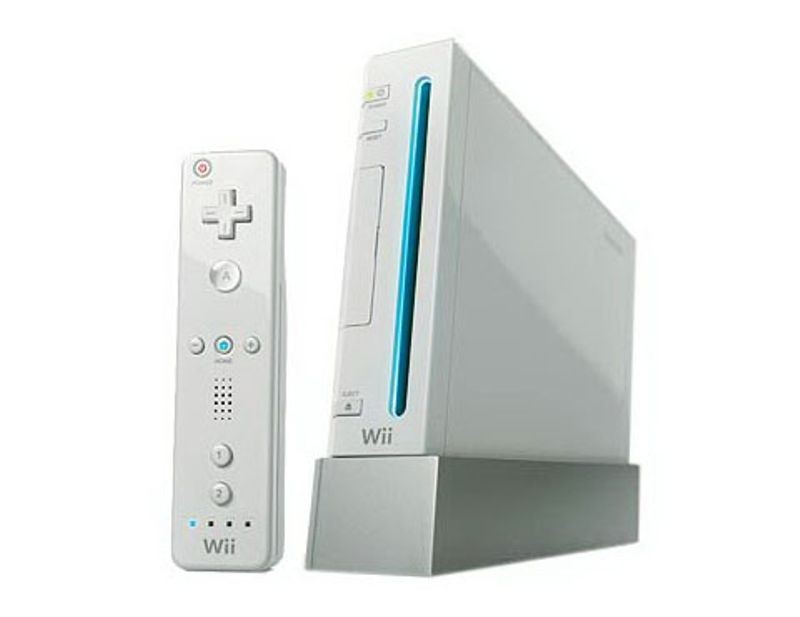

Nintendo Wii game console
Nintendo Wii comes to market
Nintendo’s Wii game system does not merely introduce new games and controllers, but new ways of interacting with game systems. The Wii Remote combined advanced gesture recognition into gaming, using accelerometer and optical sensor technologies to interact with the user. These advances allowed for games to incorporate a wide range of player physical movements. Several games came their own with specialized controllers, including Wii Fit, Wii Tennis and Wii Boxing. The Wii console also allowed access to online services providing games, news, and entertainment offerings. It has sold more than a hundred million units worldwide.
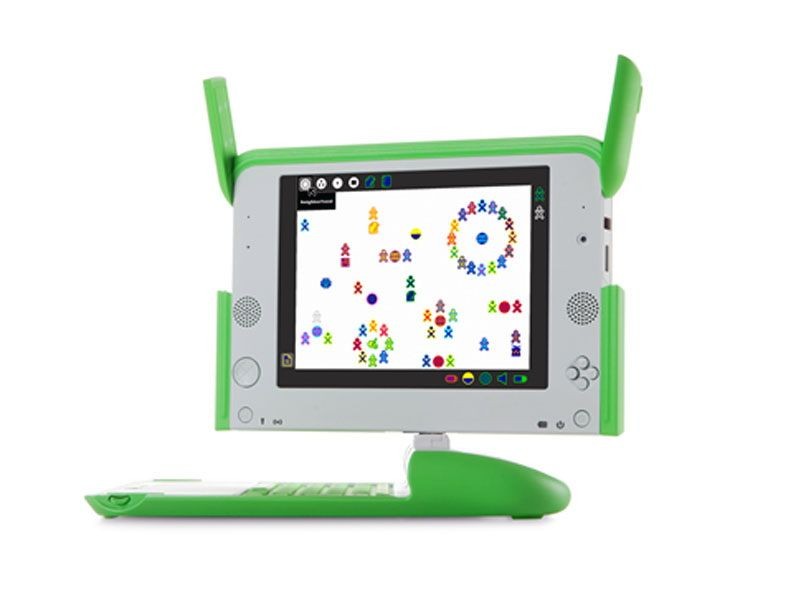

OLPC XO laptop computer
One Laptop Per Child initiative begins
At the 2006 World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) announces it will create a program to deliver technology and resources to targeted schools in the least developed countries. The project became the One Laptop per Child Consortium (OLPC) founded by Nicholas Negroponte, the founder of MIT’s Media Lab. The first offering to the public required the buyer to purchase one to be given to a child in the developing world as a condition of acquiring a machine for themselves. By 2011, over 2.4 million laptops had been shipped.

Google logo
Verb ‘to google’ added to dictionaries
First used in a private communiqué by Google co-founder Larry Page, ‘googling’ entered into the lexicon nearly as quickly as the company became the leader in Internet search. One of the earliest uses in popular culture was by the character Xander in the television program Buffy The Vampire Slayer. In 2006, both the Oxford English and Merriam-Webster dictionaries added ‘google’ as a new verb defined as “to use the Google search engine to seek online information.”
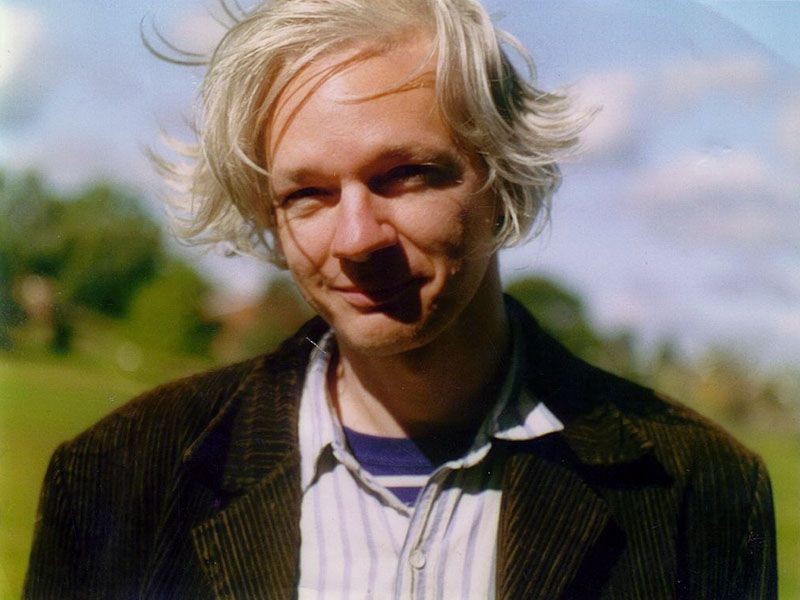

Julian Assange, 2006
WikiLeaks established
Founded by a group of journalists and chartered in Iceland, WikiLeaks serves as clearinghouse for secret information, news leaks, and anonymous material. Documents from various governments, as well as private organizations like The Church of Scientology, can be anonymously posted and distributed using WikiLeaks’ uploader. The release of more than two hundred thousand U.S. diplomatic cables beginning in 2010 has made WikiLeaks, and its founder Julian Assange, world famous.
Salesforce.com specializes in cloud computing
“The Cloud”: Computer utilities return
In the 1960s when computers were extremely expensive, a number of companies had offered what were called computer utilities. They would run your programs and store your data on their computer, which you would access with a terminal. As time went on cheaper computers had made it more economical for companies and eventually individuals to maintain their own workstations and PCs. But in the Web era, the economies of scale that evolved from large commercial Web servers had begun to tip the balance back the other way.
Starting in the mid 2000s the computer utility model starts to became fashionable again under the name “The Cloud,” and is once again a major trend in both networking and computing. Amazon’s 2006 Elastic Compute Cloud helps popularize the idea. Today, cloud-based companies offer nearly any software or service – including data storage – that could be done on a personal computer or on larger machines run by a company’s IT department.

Portal box cover
Portal is introduced
Featuring complicated puzzles, a science fiction setting, and a passive-aggressive robot named GlaDOS, Portal is designed by Valve Entertainment. Players control Chell, who used an Aperture Handheld Portal Device to solve puzzles set forth by GlaDOS, who promised a non-existent cake when they are all completed. Portal spawned a highly anticipated sequel, as well as a fan base that created real world interpretations of many of the devices shown in the game.

Checkers Championship where Chinook checkers program faced human competitors at The Computer Museum, Boston
Checkers is Solved
An article is published titled Checkers is Solved in a September issue of the journal Science. The article stated, “Perfect play by both sides leads to a draw.” The team that conducted the research was led by Professor Jonathan Schaeffer at the University of Alberta who had been working to solve the checkers problem since 1989. In the course of their work the team created a checkers program called “CHINOOK”, which played successfully in several man-machine competitions, including one held at The Computer Museum in Boston in 1994.

Typical server farm
Dropbox
Dropbox is founded by Arash Ferdowsi and Drew Houston. Dropbox was designed as a cloud-based service used for convenient storage and access to files. Users could upload files via the web to Dropbox’s vast server farms, and could instantly access them on any of their devices or computers that had the Dropbox client installed. The service also included sharing functionalities which allowed access to folders by multiple users. Dropbox’s “freemium” business model allowed limited, basic file management for free, but for users requiring higher bandwidth, a fee was charged.
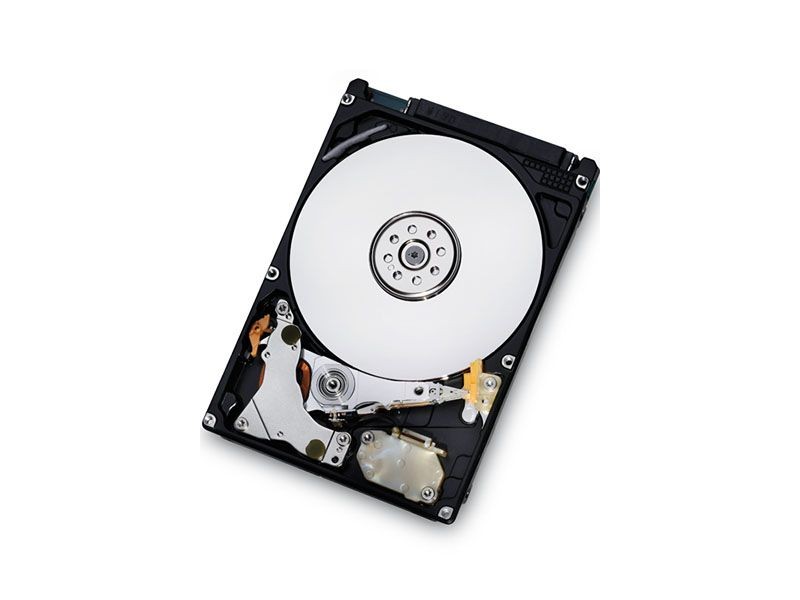

Deskstar 1TB HDD
First 1 TB hard disk drive (HDD)
Hitachi Global Storage Technologies announces the first 1 TB hard disk drive (HDD). The Hitachi Deskstar 7K1000 used five 3.5-inch 200 GB platters and rotated at 7,200 RPM. By comparison, the world’s first HDD, the IBM RAMAC 350, had a storage capacity that was approximately 3.75 MB. As such, the Deskstar had a greater storage capacity by a factor of 300,000 and was thousands of times smaller.

Hulu logo
Hulu is founded
Founded out of a rare act of cooperation between US media giants Disney-ABC Television Group, Fox Broadcasting and NBC Universal, Hulu allows users to watch streaming video content on-demand. Though only available in the US, Hulu also brought series from around the world to the service, as well as producing original content.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory Titan supercomputer that uses Cuda GPUs
Nvidia releases Cuda GPU
Graphic Processing Units (GPUs) have become an important part of multimedia computing and graphics processing. Computer Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) was a concept that allowed for GPUs to do some of the functions usually reserved for the Central Processing Unit (CPU), allowing devices and software to take advantage of the multi-threaded processing techniques and scalability of GPUs. While many saw wide applications in the games industry, uses in many scientific disciplines such as in computational biology and cryptography were also significant.
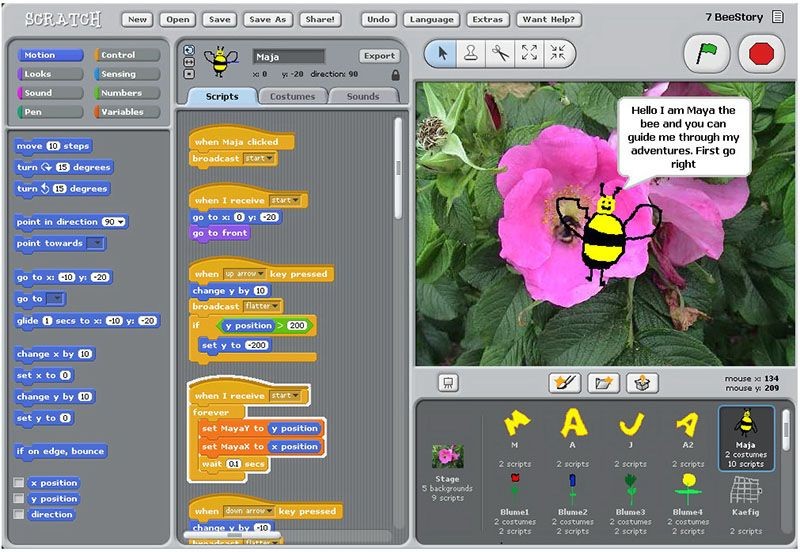
Scratch screenshot
Scratch is publicly released
Scratch is released to the public. A free programming language that focused on education, it was designed by a team led by Mitchel Resnick at the MIT Media Lab Lifelong Kindergarten Group. Intended to be used by educators, students and parents as a teaching language, it had a number of applications in educational settings. These included math, computer science, language arts and social studies. Its interface allowed novice users to stack and organize block commands to write programs. Scratch has millions of users worldwide and is available in more than 40 languages.

Amazon Kindle
The Amazon Kindle is released
Many companies have attempted to release electronic reading systems dating back to the early 1990s. Online retailer Amazon released the Kindle, one of the first to gain a large following among consumers. The first Kindle featured wireless access to content via Amazon.com, along with an SD card slot allowing increased storage. The first release proved so popular there was a long delay in delivering systems on release. Follow-on versions of the Kindle added further audio-video capabilities.
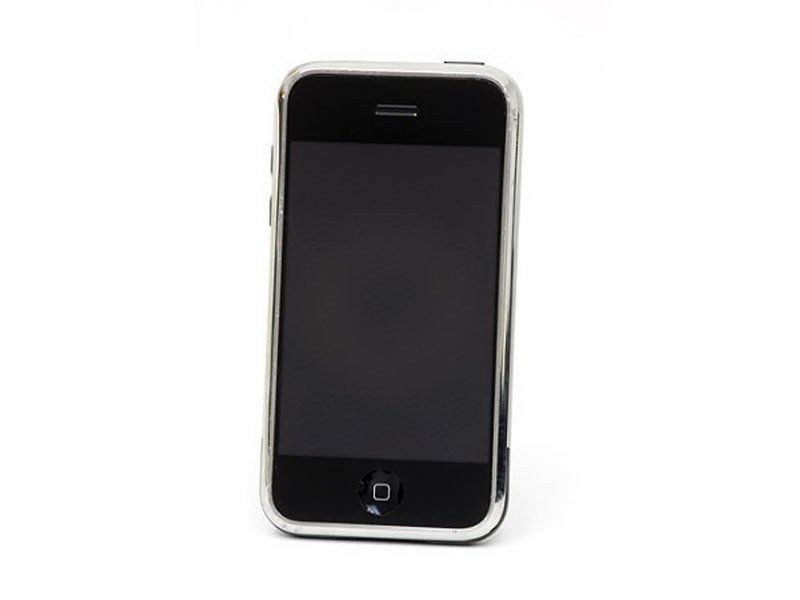

Apple iPhone
The Apple iPhone is released
Apple launches the iPhone – a combination of web browser, music player and cell phone – which could download new functionality in the form of “apps” (applications) from the online Apple store. The touchscreen enabled smartphone also had built-in GPS navigation, high-definition camera, texting, calendar, voice dictation, and weather reports.

WALL-E movie poster
WALL-E debuts
Pixar Animation Studios and Walt Disney Pictures produce the motion picture WALL-E (Waste Allocation Load Lifter-Earth Class), about a robot left to clean up Earth after humans abandon a littered and dying home planet. After more than 700 years, WALL-E has developed sentience and discovers a seedling, the first sign of new biological life on the planet. Fatefully, another robot arrives on Earth after being sent back to check for renewed signs of life and WALL-E falls in love. Working together, the two robots hold mankind’s fate in their robotic grips. The film won the Academy Award for Best Animated Feature and the Hugo award for Best Dramatic Presentation.
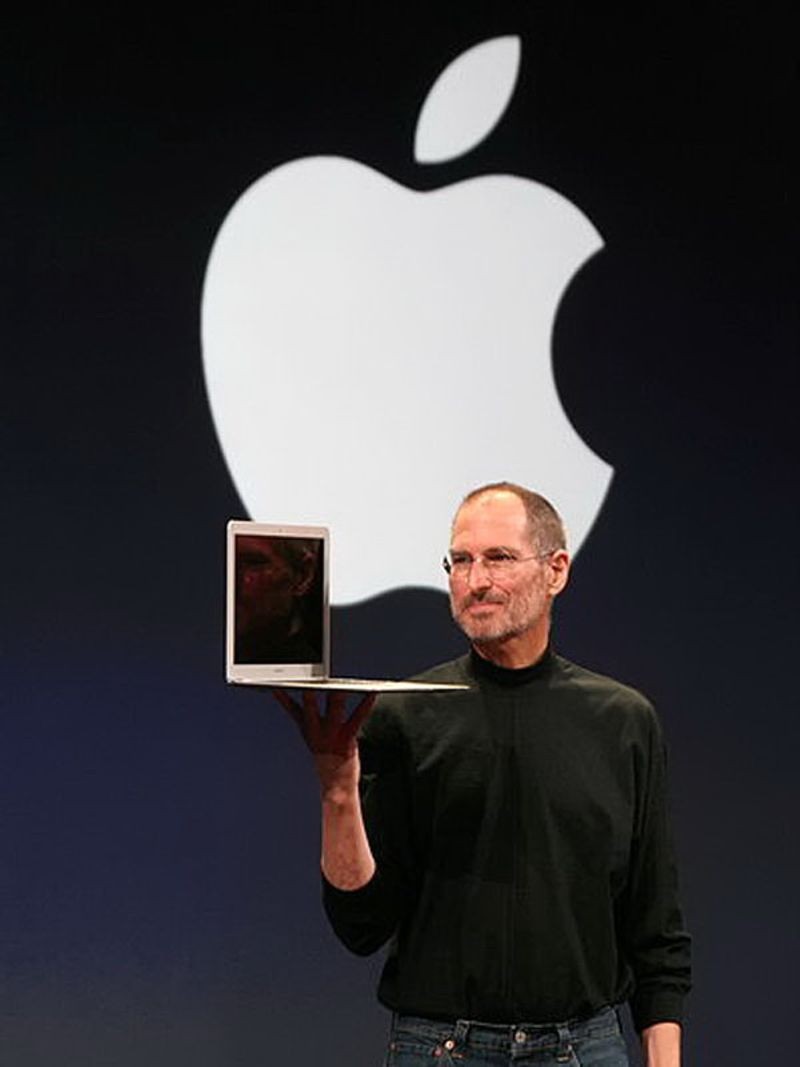

Steve Jobs introducing MacBook Air
The MacBook Air is released
Apple introduces their first ultra notebook – a light, thin laptop with high-capacity battery. The Air incorporated many of the technologies that had been associated with Apple’s MacBook line of laptops, including integrated camera, and Wi-Fi capabilities. To reduce its size, the traditional hard drive was replaced with a solid-state disk, the first mass-market computer to do so.
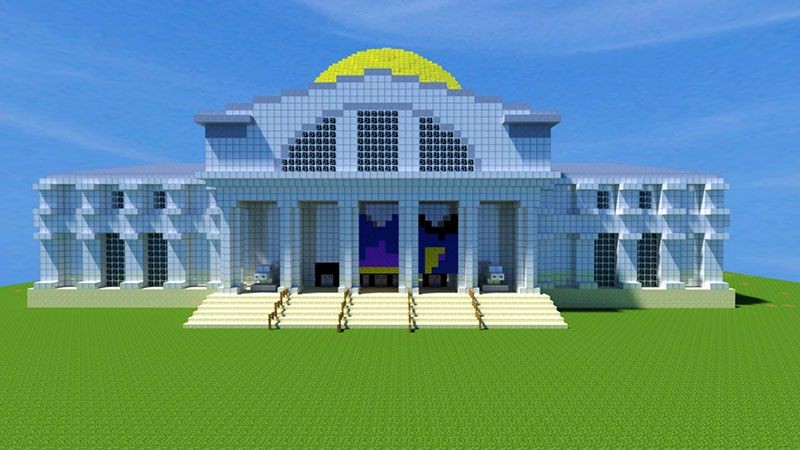

American Museum of Natural History (Brooklyn) rendered in Minecraft
Minecraft is introduced
Initially developed by Swedish game designer Markus “Notch” Persson, Minecraft allows players to build towers and play challenges. The game, which could be played in either survival or creative mode, has received many awards from the international gaming press. An enormous variety of physical systems and machines can also be built in the Minecraft environment, taking the game far beyond its intended use as a simple entertainment platform into a flexible and creative building system for modeling real-world processes or things. Users have built entire computers, cities, and even planets out of Minecraft components.

Plants vs. Zombies screenshot
Plants vs. Zombies is released
Initially conceived as a game that would walk the line between gritty and sickeningly cute, programmer George Fan develops Plants vs. Zombies for PopCap Games. Influenced by ‘tower defense games’ where players attempt to repel attackers, Plants vs. Zombies gave players a chance to turn back an invasion of the Undead using cartoon household plants. The game was ported to many different systems, including the iPad, Steam, and PlayStation 3.
Bitcoin
In 2008, “Satoshi Nakamoto,” likely a pseudonym, publishes Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System, describing the use of peer-to-peer networks to generate a “crypto-currency.” In the Bitcoin system, users run software that searches for blocks of data, the discovery of which reward the users with Bitcoins. The transaction is recorded on the system though user information is private. These can then be used online much like cash in the real world. Nakamoto ‘mines’ the first Bitcoins in January 2009 and a year later a user used them to order two pizzas. Bitcoins’ value exploded in November 2013 before a gradual devaluation. Bitcoin’s anonymous nature, along with the electronic nature of the currency, has led to its adoption by some criminal organizations.
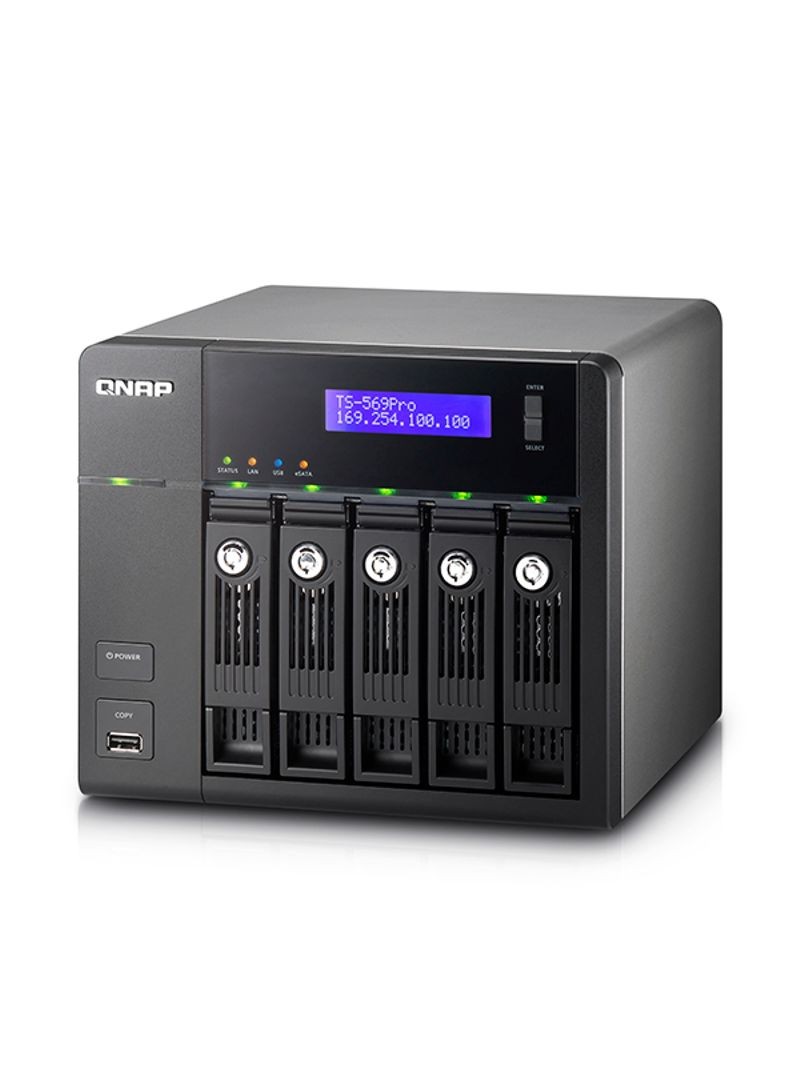

Typical cloud-based NAS storage array
Cloud-based network-attached storage solutions
Vendors announce cloud-based network-attached storage solutions for online backup. They were designed for small and medium sized businesses in addition to general consumers. With these services, servers could automatically back up data to remote servers. They were designed for data protection, and along with backup capability it also provided a data recovery solution.
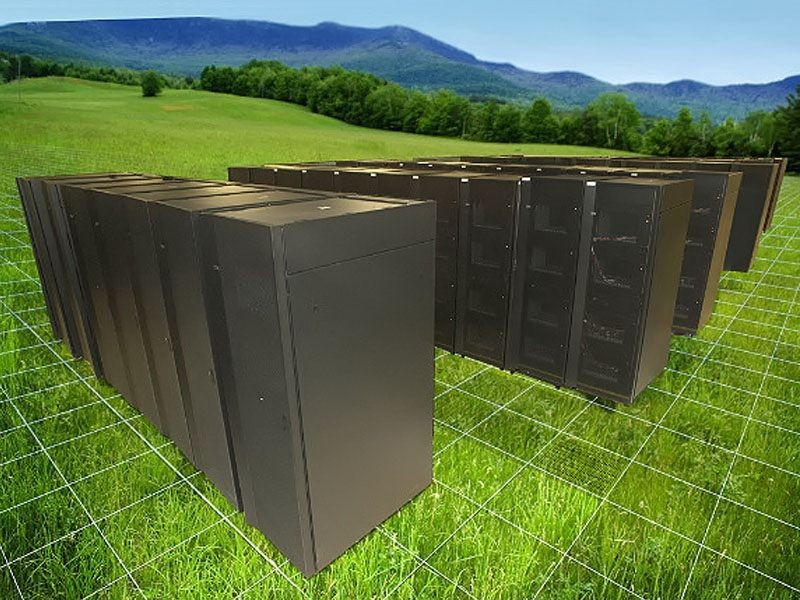

Computer-enhanced image of IBM’s Roadrunner
IBM’s Roadrunner supercomputer is completed
The Roadrunner is the first computer to reach a sustained performance of 1 petaflop (one thousand trillion floating point operations per second). It used two different microprocessors: an IBM POWER XCell L8i and AMD Opteron. It was used to model the decay of the US nuclear arsenal, analyze financial data, and render 3D medical images in real-time. An offshoot of the POWER XCell8i chip was used as the main processor in the Sony PlayStation 3 game console.
Jaguar Supercomputer at Oak Ridge upgraded
Originally a Cray XT3 system, the Jaguar is a massively parallel supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, a US science and energy research facility. The system cost more than $100 million to create and ran a variation of the Linux operating system with up to 10 petabytes of storage. The Jaguar was used to study climate science, seismology, and astrophysics applications. It was the fastest computer in the world from November 2009 to June 2010.

App Store
The Mobile Web hits the Mass Market
By the late 2000s, 3G networks for higher speed mobile data had been spreading fast. The iPhone’s phenomenal popularity creates a new computing platform that brings mobile Web browsing to a large audience. Google’s Android mobile platform soon makes that audience even larger. The App store model used by the iPhone and then Android is based on Apple’s earlier success with iTunes. But because proprietary apps run directly over the Internet, they are not part of the public Web – and present a risk of fragementing it as a standard.